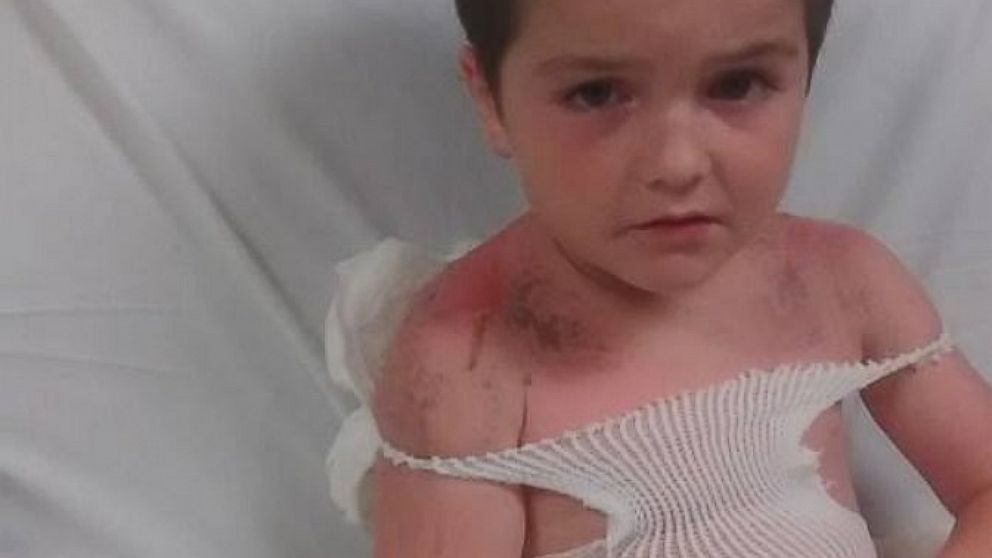
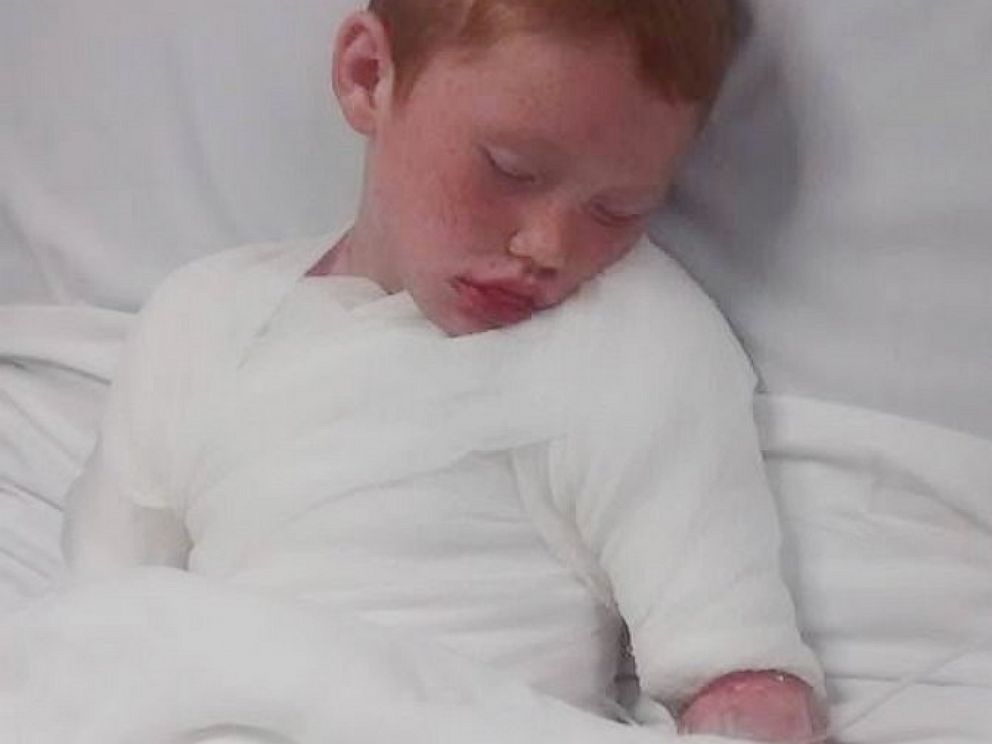
Quicker and faster 3-D printers have allowed not just amazing objects to be created, seemingly out of nothing, but have started to affect how doctors and medical providers treat patients.
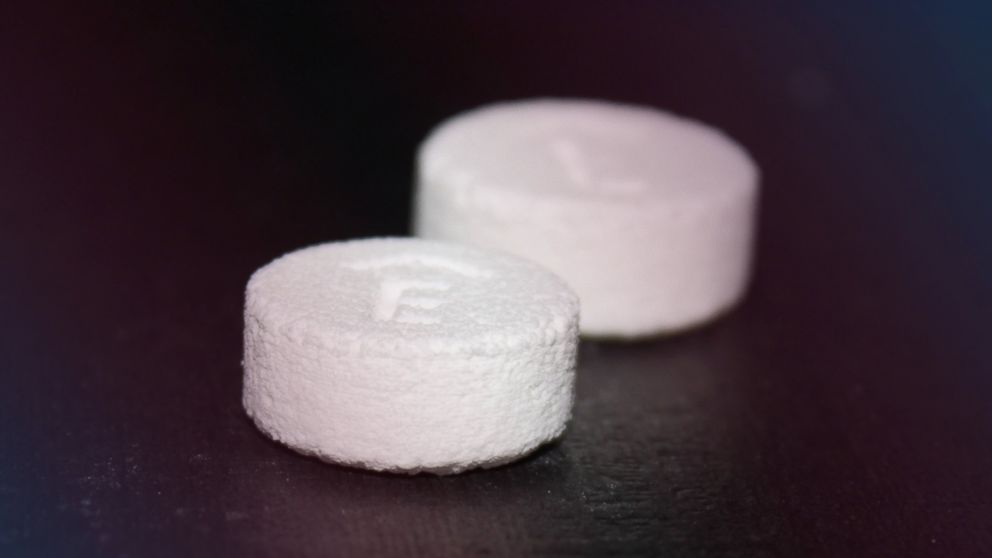
This week, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced the approval of the first 3-D printed pill. The tablet, called Spritam, is designed to help treat epilepsy and is created through a layered 3-D printing process that lets the tablet dissolve once taken with water.
Spritam is just the latest medical treatment to utilize 3-D printing. Doctors and medical providers have been starting to use the handy device to do everything from create models for trachea or windpipes to create “tiny livers” that can test new medications.
We’ve put together a list of some of the most amazing medical breakthroughs made possible with 3-D printing.
“Tiny Livers” Could Help Test New Medications
Last year, a San Diego company announced they had managed to “bio-print” tiny livers with a specially designed 3-D printer. The tissue they “print” is combined with three kinds of human liver cells and is designed to allow researchers to test new medications without involving a human patient.
Life-Saving Airway
In 2013, doctors painstakingly created a new airway for an Ohio boy who had been born with abirth defect that left him gasping for air.
Kaiba Gionfriddo was born with a defective airway that kept collapsing. To save his life doctors printed tiny tubes to fuse together in different shapes and sizes until one finally worked for Kaiba. The splint was placed in Kaiba’s bronchus so that it no longer collapsed. Even more remarkably, once the plant was placed it could stay there. It is designed to eventually be absorbed into the body.
New "Bionic" Hands
One of the most remarkable ways 3-D printing is now being used is as a way to create cheaper prosthetics.
A boy born without an arm named Alex was able to get a new “bionic” hand thanks to the help of a few innovative university students and a 3-D printer. Last year at the University of Central Florida student spent 8 weeks coming up with a special prosthetic design that only cost a few hundred dollars in raw materials. They said they wanted to create a model prosthetic far cheaper than the other options that can run tens of thousands of dollars.